Cycling Calculators
About
This wonderful website, made with ❤️ by , aggregates useful cycling calculators for enthusiasts and professionals alike. If you find it helpful, please feel free to share it with others who might benefit from it, and don't forget to bookmark it in your shortcut bar!
These cycling calculators are free, and they always will be, but it costs me money to host and renew the domain name. If you want to support my work and encourage me to add more calculators, please consider sponsoring me.
Who I am?
Hello! My name is Ferran Figueredo and, since 2018, I've been dedicating a small part of my time to sharing my passion for cycling and exploring how technology and data are transforming the world of contemporary cycling.
If you're a cycling enthusiast, an avid rider, or simply someone interested in the exciting intersection of cycling and technology, you've come to the right place.

Found a bug? A missing calculator?
If you need a cycling calculator that is currently not present here, or you found a bug, or something doesn't work as expected, you can contact me at .
Bike Position on Road Bike
Having the right bike position is crucial for every cyclist. It can help you to avoid injuries and improve your performance. Use our Bike Position Assistant to find out what is your ideal bike position and what problems you may have with your current bike setup.
Calories Burned Calculator
Calories Burned Calculator estimates the energy expenditure during cycling exercise based on your power output and duration.
Knowing how many calories you burn during a cycling workout is crucial for planning your nutrition and hydration strategy.
Carbohydrates Calculator
Carbohydrates Calculator helps you to calculate the amount of carbohydrates you need to consume during a cycling workout to maintain your energy levels and avoid bonking.
Compound Score Calculator
The "Compound Score" in elite road cycling, is a metric designed to evaluate a cyclist's performance by combining both absolute and relative power outputs.
Compound Score combines absolute and relative power, accounting for both strength and weight efficiency. This dual approach offers a more comprehensive performance assessment, especially in varied terrain, making it more accurate than FTP alone.
Critical Power Calculator
CP is the power output that you'll trend towards when riding at a high intensity, as exercise duration is increased "indefinitely". "Indefinitely" is a mathematical construct, and not actually true in practice. People can typically only sustain power outputs at CP for around 30-minutes.
W' (measured in kJ – i.e. units of energy) is the amount of work that can be done above the CP.
Cycling Nutritionist
Our cycling nutritionist assistant will help you answer all the questions about your nutrition and hydration during cycling. Get answers about (or design) a nutrition plan, hydration, recovery, or weight loss to improve your cycling performance.
Efficiency Factor Calculator
Efficiency factor (EF) is the ratio of Normalized Power to heart rate. An increase in this value for steady-state, aerobic endurance intensity rides may indicate an improvement in aerobic fitness.
The Efficiency Factor Calculator measures how effectively a cyclist converts energy into forward motion by comparing normalized power to heart rate. This metric helps cyclists identify how efficiently they're performing at various intensities.
A higher efficiency factor indicates better energy utilization, which is crucial for long rides and racing.
EPOC Calculator
EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption) is the amount of oxygen consumed during recovery after a cycling workout. EPOC is a key indicator of the intensity and the effectiveness of your training.
Functional Threshold Power Calculator
Functional Threshold Power (also called FTP) is one of the most important metrics used in cycling. It is the maximum amount of power that can be sustainably produced for one hour, measured in watts.
This is one of the most important values in sports performance testing because it is a benchmark that can be used to measure fitness and predict performance. Knowing your functional threshold power is crucial for every cyclist, pro or amateur.
Heart Rate Zones Calculator
Heart Rate Zones are a set of five training levels based on the percentage of your Maximum Heart Rate (MHR). Each zone is designed to target specific physiological adaptations and improve your cycling performance.
Intensity Factor Calculator
The Intensity Factor (IF) represents the ratio of a workout's intensity relative to the cyclist's maximum sustainable effort, typically measured by Functional Threshold Power (FTP). By calculating IF, cyclists can better understand how hard a ride was in comparison to their personal max effort, allowing them to fine-tune training loads to avoid overtraining or undertraining.
For instance, an IF of 0.75-0.85 suggests a moderate endurance workout, while values around 0.9 or higher indicate intense efforts. Using IF, cyclists can adjust upcoming workouts based on previous intensities, helping to balance recovery and prevent fatigue, while progressively pushing limits for optimized performance gains.
Maximum Heart Rate Calculator
Maximum Heart Rate (MHR) is the highest number of heartbeats per minute that your body can reach during intense exercise. Knowing your maximum heart rate is important for setting training zones and monitoring your exercise intensity.
Power / Heart Rate Calculator
The Power vs. Heart Rate Ratio Calculator evaluates the relationship between power output and heart rate, offering insight into aerobic efficiency. A lower ratio over time suggests improved fitness, as the cyclist can generate more power at a lower heart rate.
Monitoring this ratio helps cyclists adjust their training to enhance endurance, track fatigue, and optimize cardiovascular efficiency, ensuring better long-term performance.
Power to Weight Ratio Calculator
The Power to Weight Ratio Calculator helps cyclists determine how many watts of power they generate per kilogram of body weight. This metric is crucial in assessing climbing ability and overall performance, as a higher power-to-weight ratio typically translates to better speed on climbs and improved endurance.
Tracking this ratio helps cyclists fine-tune their training to either increase power, reduce weight, or both, for more efficient performance gains on challenging terrains.
Power Zones Calculator
Power Zones are a set of seven training levels based on the percentage of your Functional Threshold Power (FTP). Each zone is designed to target specific physiological adaptations and improve your cycling performance.
Recovery Time Calculator
Recovery Time is the time needed to recover from a cycling workout. It is important to know how long it will take to recover from a workout to avoid overtraining and injuries.
Sport Psychologist
Our sport psychologist assistant will help you answer all the questions about your mental preparation and performance during cycling. Get answers about mental preparation, performance anxiety, motivation, or stress management to improve your cycling performance.
Sports Drink Calculator
Sports Drink Calculator helps you to create your own homemade sports drink to keep you hydrated and energized during your cycling workouts.
Add lemon juice or other flavors to your homemade sports drink to make it more enjoyable.
Strava+ Insights
Use our tool to analyze your Strava activities and get insights into your cycling performance. Our tool will help you to improve your cycling performance and achieve your goals.
Get Started with Strava+ Insights
How it works?
We use AI to analyze data from your activities, including health and location data, to create relevant summaries that appear on your activities.
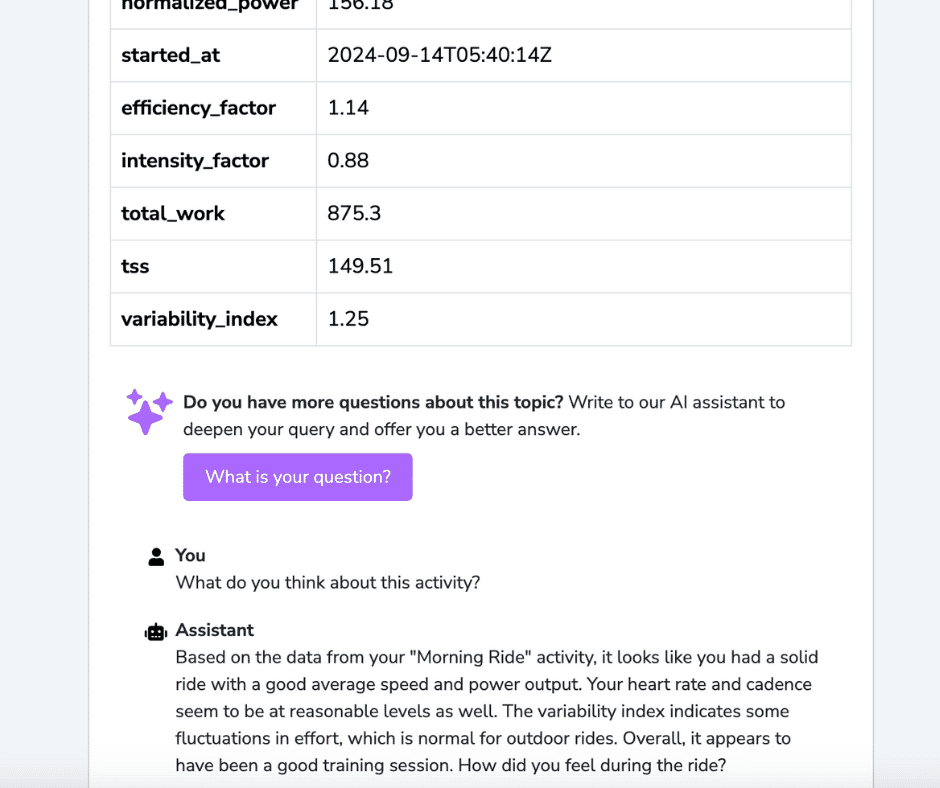
You can ask questions to our assistant for a more detailed analysis of this activity. Scroll down to your activity stats for further questions on stats such as elevation, pace/speed, Grade Adjusted Pace, heart rate, heart rate zones, and pace/power zones.
Is it free?
You need to become a Supporter to use this tool. It costs only $4/month. Becoming a Supporter will also help you to cover hosting costs and fund more developments. Remember that you can cancel at any time.
Total Work Calculator
Total Work is the amount of work done during a cycling workout. Total Work represents the total amount of energy expended during a workout and is measured in kilojoules (kJ).
This is particularly useful for gauging calorie burn, assessing workout load, and planning recovery needs. By tracking total work, cyclists can manage training intensity and duration more effectively, align nutrition strategies, and build endurance through tailored energy output goals.
TRIMP Calculator
TRIMP (TRaining IMPulse) is a method for quantifying the training load of a workout. It is a measure of the intensity and the duration of an activity.
Training Stress Score Calculator
The Training Stress Score Calculator provides a method for estimating the intensity and the resulting physiological stress of a training session. Enter Duration, Normalized Power and your FTP to calculate Training Stress Score of your cycling workout.
VAM Calculator
VAM (Velocità Ascensionale Media) is a measure of your climbing speed. It is the average ascent speed in meters per hour. VAM is a key indicator of your climbing performance.
VAM to Power Calculator
VAM to Power Calculator helps you to convert your climbing speed (VAM) to power output in watts. Enter your weight and VAM to get power output in watts.
VAM to VO2 Max Calculator
VAM to VO2 Max Calculator helps you to convert your climbing speed (VAM) to VO2 Max. Enter your weight and VAM to get VO2 Max in ml/kg/min.
Variability Index Calculator
Variability Index (VI) measures how smooth (evenly paced) or variable (with frequent changes) was your power output during your ride. A high variability index indicates erratic pacing, which can lead to premature fatigue and reduced performance.
By analyzing this metric, cyclists can fine-tune their pacing strategies, ensuring more efficient energy use and improved endurance. Ultimately, it helps cyclists achieve more consistent performances and reach their training goals effectively.
VO2 Max Calculator
VO2 Max is the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use during intense exercise. It is a key indicator of your cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance.